 When driving electromechanical devices, the current can be significantly higher than normal for short durations, often lasting for hundreds of milliseconds or a few seconds at the very most. A good alternative to adding up the total maximum powers used in your application, is to select a power supply with a peak power rating. These have the ability to exceed their normal power ratings for short periods without going into over current protection. A major concern of engineers is system lifetime. The peak power requirements typically have a very minor impact on power supply average operating component temperature and so have little impact on lifetime.
When driving electromechanical devices, the current can be significantly higher than normal for short durations, often lasting for hundreds of milliseconds or a few seconds at the very most. A good alternative to adding up the total maximum powers used in your application, is to select a power supply with a peak power rating. These have the ability to exceed their normal power ratings for short periods without going into over current protection. A major concern of engineers is system lifetime. The peak power requirements typically have a very minor impact on power supply average operating component temperature and so have little impact on lifetime.
Understanding peak power allows you to optimise your power supply selection. Power supplies are rated with either a convection cooled and/or fan cooled rating and some with a peak power rating. The peak ratings are specified for a limited period of time and for a maximum duty cycle. The duty cycle is defined as a percentage of the total operating time. When using peak power, it is important to make sure the average power rating does not exceed the continuous power rating.

 For example purposes consider our 3 x 5” package VKR300. It has a convection rating of 200W, a fan cooled rating of 300W and a peak rating of 400W. The peak rating can last for 5s at a max duty cycle of 10%.
For example purposes consider our 3 x 5” package VKR300. It has a convection rating of 200W, a fan cooled rating of 300W and a peak rating of 400W. The peak rating can last for 5s at a max duty cycle of 10%.
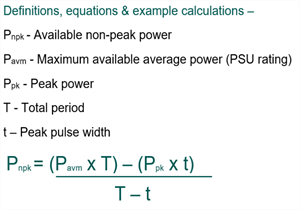
Using the VKR300 ratings for the example; it is useful for an engineer to be able to calculate what the available non-peak power is, knowing his peak power requirements. For this example, we will consider the customer’s application as 400W peak for 5sec, duty cycle 10%. So “T” equals 5/0.1=50sec. 200W convection rating maximum continuous power.
So the non-peak available convection cooled power equals 178 Watts.
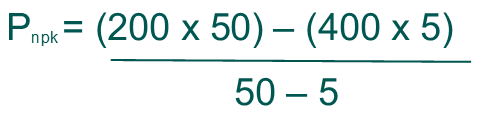 In this situation you have selected a 200W convection cooled power supply, considered your peak power, understand that the non-peak power is 178W and that it can cope with a 400W peak for 5sec with a 10% duty cycle. The designer who just adds up his maximum requirements will specify a 400W power supply, which will be 50-70% higher cost and with a larger form factor. The pressure for modern designers to achieve high quality, reliable solutions at a good price has increased. Considering the load like this will give large benefits to your design.
In this situation you have selected a 200W convection cooled power supply, considered your peak power, understand that the non-peak power is 178W and that it can cope with a 400W peak for 5sec with a 10% duty cycle. The designer who just adds up his maximum requirements will specify a 400W power supply, which will be 50-70% higher cost and with a larger form factor. The pressure for modern designers to achieve high quality, reliable solutions at a good price has increased. Considering the load like this will give large benefits to your design.
If you know both your peak and non-peak power levels and duration and duty cycle you can calculate your average power and verify if it exceeds the maximum rating of your possible power supply selection. The equation for this is below –

Where pav is the average power of the application and T1 is the duration of non-peak power.
Click here to download this article in PDF.
See more at: http://www.fiduspower.com/
